2nd International Conference on Non-invasive Cardiac Imaging, Nuclear Cardiology & Echocardiography
Amsterdam, Netherlands

Valéria Paula S. Fazan
University of São Paulo ,Brazil
Title: Evidence of a hypertensive peripheral neuropathy in an experimental model of hypertension in rats
Biography
Biography: Valéria Paula S. Fazan
Abstract
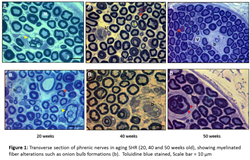
Statement of the Problem: Spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR), first inbred from Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY), are considered a good experimental model of human essential hypertension. Hypertension is a main risk factor for stroke and vascular dementia and may cause important changes to the cerebrovascular tree, turning the brain more susceptible to infarcts, microaneurysms and ischemia. In spite of the well documented influence of hypertension on the brain, data on the sensitivity of peripheral nerves in hypertension is scarce. The purpose of this study was to investigate the alterations on the morphology and morphometric data on sural, phrenic and vagus nerves of adult SHR, with well-established hypertension.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: Male and female SHR and normotensive WKY rats aged 20 weeks (N = 6 in each group) were investigated. After arterial pressure and heart rate recordings in anesthetized animals, right and left sural nerves were removed and prepared for epoxy resin embedding and light microscopy. Morphometric analysis was performed with the aid of computer software, and took into consideration the fascicle area and diameter, as well as myelinated fiber number, density, area and diameter.
Findings: Significant differences were observed for the myelinated fiber number and density, comparing different genders of WKY and SHR in all nerves. Also, significant differences for the morphological (thickening of the endoneural blood vessel walls and lumen reduction) and morphometric (myelinated fibers diameter and G ratio) parameters of myelinated fibers were identified.
Conclusion & Significance: Morphological exam of the myelinated fibers suggested the presence of a neuropathy due to hypertension in both SHR genders. These results indicate that hypertension altered important morphometric parameters related to nerve conduction in hypertensive animals. Moreover the comparison between males and females of WKY and SHR showed that the morphological and morphometric alterations due to hypertension are not gender related.
References:
- Da Silva GA, Mendes VA, Genari AB, Castania JA, Salgado HC, Fazan VPS (2016), Recurrent laryngeal nerve alterations in developing spontaneously hypertensive rats. Laryngoscope 126(1):E40-7
- Sanada LS, Tavares MR, Sato KL, Ferreira R da S, Neubern MC, Castania JA, Salgado HC, Fazan VPS (2015) Association of chronic diabetes and hypertension in sural nerve morphometry: an experimental study. Diabetol Metab Syndr 7:9.
- Oliveira FS, Nessler RA, Castania JA, Salgado HC, Fazan VPS (2013), Ultra structural and morphometric alterations in the aortic depressor nerve of rats due to long-term experimental diabetes: effects of insulin treatment. Brain Res 1491:197-203.
- Sanada LS, da Rocha Kalil AL, Tavares MR, Neubern MC, Salgado HC, Fazan VPS (2012), Sural nerve involvement in experimental hypertension: morphology and morphometry in male and female normotensive Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). BMC Neurosci 13:24
- Rodrigues AR, Ferreira RS, Salgado HC, Fazan VPS (2011) Morphometric analysis of the phrenic nerve in male and female Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Braz J Med Biol Res 44(6): 583-591.



